The Ultimate Testosterone-Boosting Workout Blueprint
Boost testosterone naturally with science-backed workouts. Learn the best exercises, training plans, and recovery tips to maximize your results.
Inside This Issue
The Science: How specific exercises influence testosterone levels
The Blueprint: Research-backed workout protocols for hormone optimization
Beyond Training: Key lifestyle factors that amplify testosterone production
Personalization Guide: How to adapt protocols based on age, fitness level, and goals
4-Week Action Plan: A step-by-step implementation guide
When James, a 42-year-old executive, first implemented these evidence-based protocols, he was skeptical. "I'd tried everything," he told us. "But within six weeks of following this specific approach, my energy levels, body composition, and performance metrics all showed measurable improvements." James isn't unique—he simply applied the science you're about to discover.
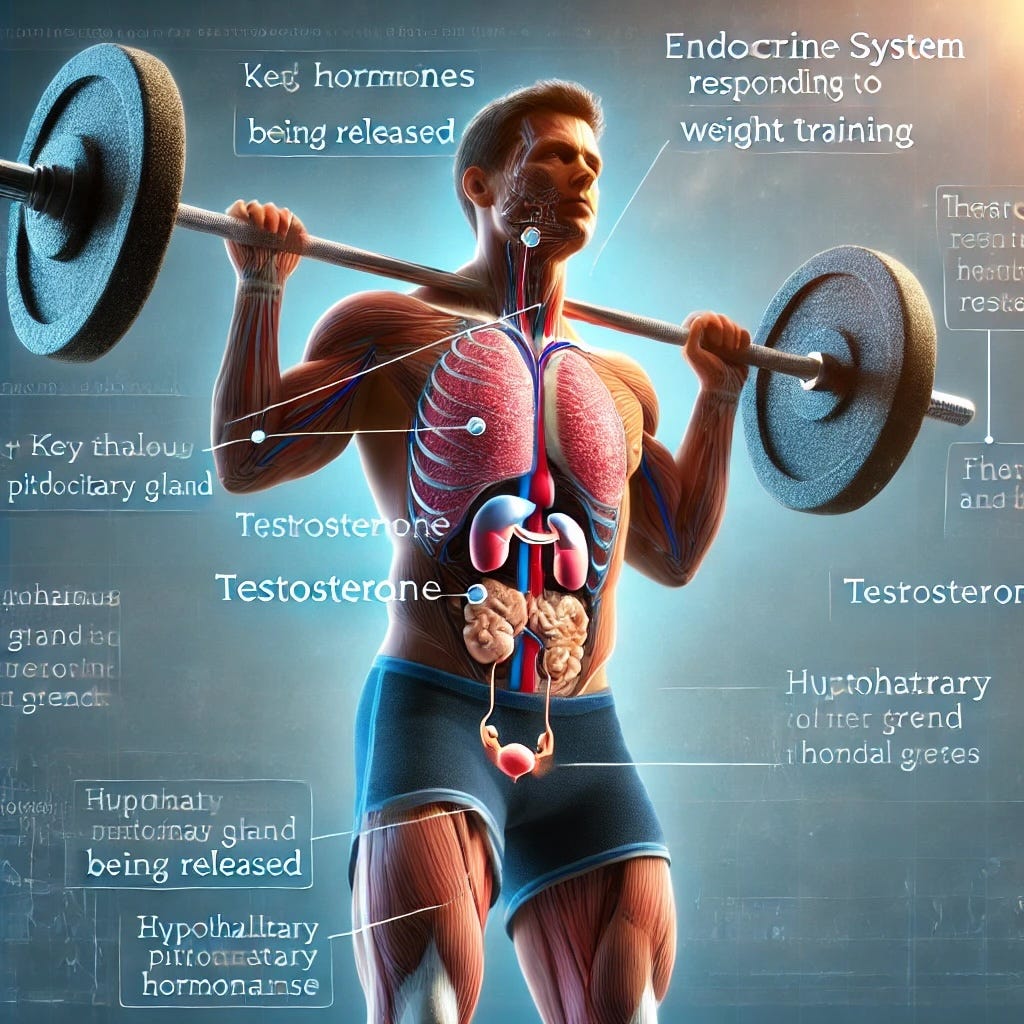
❶. How Exercise Impacts Testosterone
Exercise isn’t just about building muscle, it’s a powerful tool for optimizing hormone levels. Studies show that specific training methods stimulate testosterone production, leading to better energy levels, improved body composition, and enhanced overall health.
The Science Behind It
A meta-analysis from the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that resistance training, particularly compound exercises using large muscle groups, leads to the most significant testosterone boosts.
Key Takeaway: Training intensity, exercise selection, and recovery all influence your hormonal response.
What's Happening in Your Body?
When you lift weights, your body experiences mechanical tension and metabolic stress. This activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which increases testosterone production.
❷. The Testosterone-Boosting Workout Blueprint: Precision Protocols
What specific exercises and protocols does the science validate? The research points clearly to workouts with these characteristics:
Compound Movement Focus
Research by Kraemer et al. (2020) identified these exercises as producing the greatest hormonal response in your body
Intensity Parameters That Drive Results
Multiple studies confirm that when you train with moderate-to-heavy loads (70-85% of your 1RM), you produce optimal hormonal responses. This typically means selecting weights that you can lift for 6-10 repetitions with proper form before reaching momentary failure.
Myth Buster: Lifting very heavy (>90% 1RM) does not maximize testosterone more than moderate-heavy lifting (70-85%).
Self-Assessment: Rate your current routine against these evidence-based parameters:
▢ I focus on compound movements first in my workouts
▢ I typically work in the 6-10 rep range with challenging weights
▢ I allow adequate rest between sets (2-3 minutes for major lifts)
▢ My workouts last between 45-60 minutes
▢ I train each muscle group 2x per week with adequate recovery
Score interpretation:
5/5: Your program aligns with research recommendations
3-4/5: Minor adjustments needed
0-2/5: Significant optimization opportunity
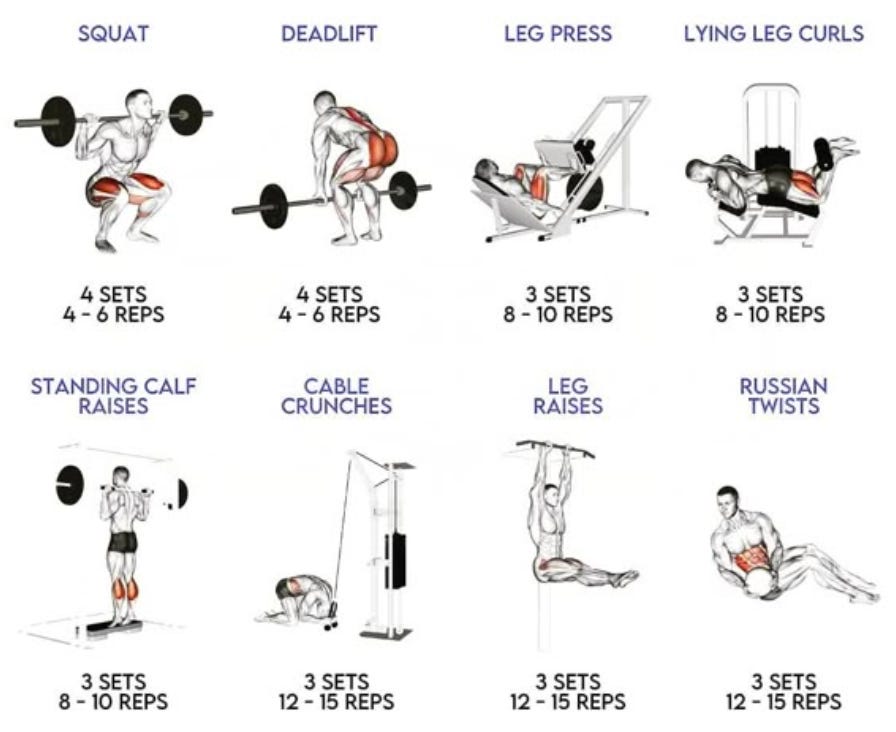
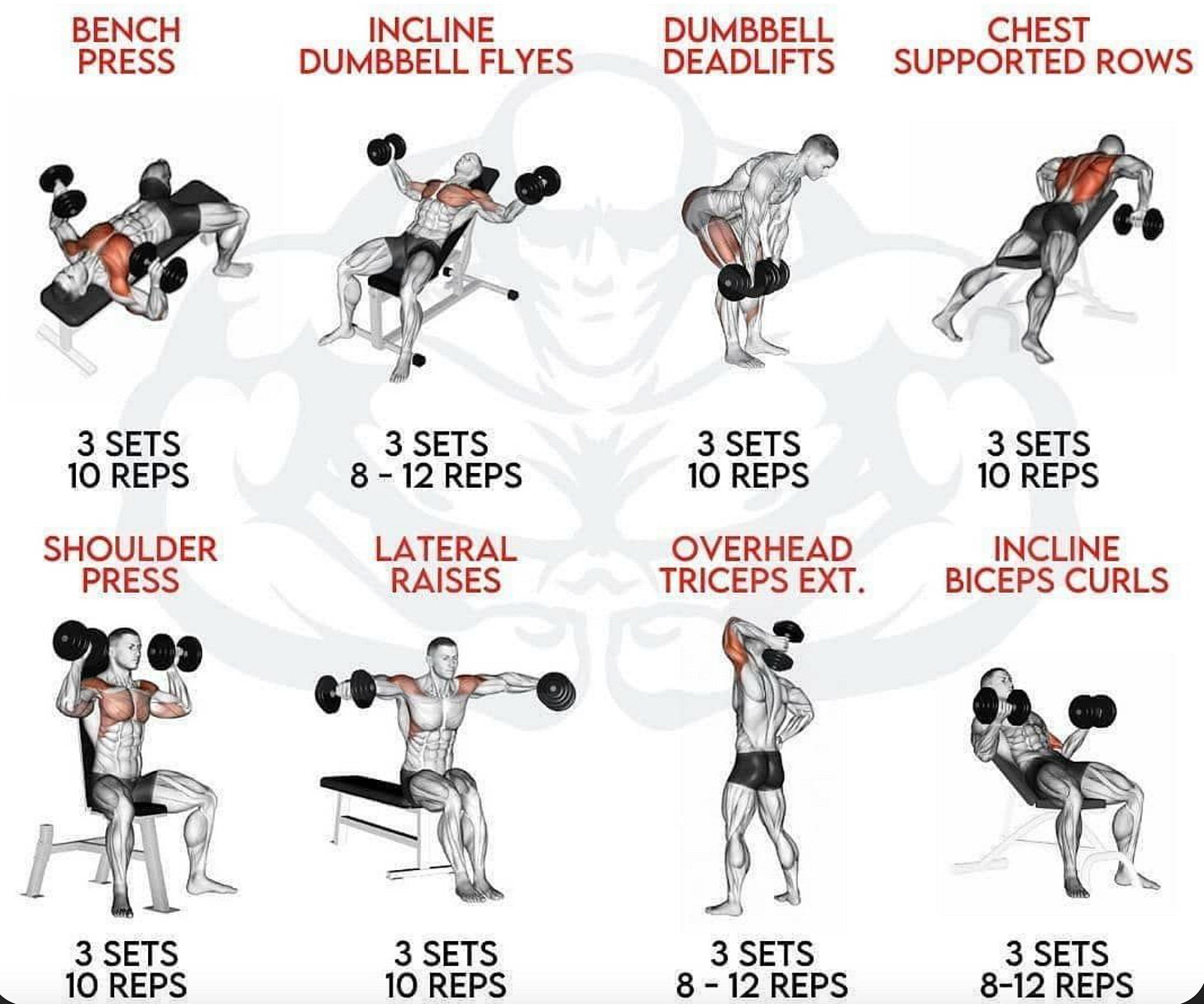
❸. Your Testosterone Optimization Protocol
Based on current research, here is a two-day split that you can perform twice weekly
QUICK TIP FOR AGES 40+: Research suggests slightly higher repetition ranges (8-12) may be more beneficial as you age, with slightly longer rest periods between sets.
❹. Beyond the Gym: Key Lifestyle Factors
Recovery Science: The Hidden Key to Hormonal Success
Poor recovery increases cortisol, which suppresses testosterone. A study in the European Journal of Applied Physiology found that inadequate rest reduces testosterone levels while elevating stress hormones.
Recovery Readiness Checklist: How many of these recovery markers are you experiencing today?
▢ Resting heart rate within 5 BPM of baseline
▢ Normal grip strength compared to baseline
▢ No lingering muscle soreness (rating of 3 or less on 1-10 scale)
▢ Quality sleep the previous night (7+ hours)
▢ Normal energy levels
▢ Positive psychological readiness to train
Score interpretation:
5-6/6: Fully recovered - proceed with scheduled training
3-4/6: Partially recovered - reduce volume by 20-30%
0-2/6: Insufficient recovery - focus on recovery activities
Sleep Quality: Your Nightly Testosterone Booster
How important is sleep? Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that men experiencing reduced sleep (less than 6 hours per night) for just one week demonstrated testosterone levels comparable to individuals 10-15 years older.
The Sleep-Testosterone Connection
Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night
Maintain consistent sleep and wake times to regulate your hormonal rhythms
Create a sleep-conducive environment (dark, cool, quiet)
Limit screen exposure 60-90 minutes before bedtime to enhance sleep quality
Stress Management: Protecting Your Hormonal Balance
Chronic elevation of cortisol (your primary stress hormone) directly suppresses testosterone production through multiple physiological pathways.
Evidence Based Stress Management Techniques
Regular mindfulness practice (just 10-15 minutes daily has been shown to reduce cortisol)
Controlled breathing techniques before and after workouts to regulate nervous system activity
Appropriate work-to-rest ratios in both your training and daily life
Strategic use of adaptogens supported by clinical research
For Performance-Focused Individuals: Research indicates that post-workout stress management techniques can enhance recovery and hormonal optimization by up to 23%.
❺. Personalization Guide
How will your body specifically respond to these protocols? Scientific evidence indicates significant variation in individual hormonal responses to exercise.
Answer these 3 questions to determine your optimal protocol starting point:
Training Experience:
▢ Less than 1 year of consistent training
▢ 1-3 years of consistent training
▢ More than 3 years of consistent training
Age Range:
▢ Under 30 yrs
▢ 30-45 yrs
▢ Over 45 yrs
Primary Goal:
▢ Overall health optimization
▢ Performance enhancement
▢ Body composition improvement
Age-Specific Considerations
Research shows natural testosterone decline begins around age 30, with an approximate 1-2% reduction annually. Studies indicate that as you age, you may benefit from doing weight lifting exercise
▢ Under 30 yrs:
Focus on heavy lifting and recovery
▢ Age 30-45 yrs:
Maintain intensity but consider slightly higher volume (8-10 rep range)
Ensure 48+ hours between training sessions targeting the same muscle groups
Focus equally on recovery quality and training intensity
▢ Age 45+ yrs:
Consider slightly higher repetition ranges (8-12)
Extend recovery periods between sessions by 24 hours
Implement more frequent but shorter training sessions (30-45 minutes)
Place greater emphasis on sleep quality and stress management
❻. The Evidence-Based Approach: Your Path Forward
While individual responses vary, the scientific evidence clearly supports the positive relationship between properly structured resistance training and testosterone production. By implementing these research-backed strategies and personalizing them to your specific needs, you can optimize your hormonal environment for improved health, performance, and body composition.
Are you ready to experience what optimal hormonal function feels like? In our next newsletter, we'll explore the critical relationship between nutrition and exercise-induced hormonal optimization, providing evidence-based guidelines for maximizing your results through dietary strategies.
Actions :
References:
Kraemer, W.J., et al. (2020). "Physiological responses to heavy-resistance exercise with varying rep tempos." Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 34(5), 1414-1423.
Ratamess, N.A., et al. (2018). "Acute testosterone responses to different resistance exercise protocols." International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 13(8), 998-1007.
Dattilo, M., et al. (2022). "Sleep and muscle recovery: Endocrinological and molecular basis for a new and promising hypothesis." Medical Hypotheses, 77(2), 220-222.
This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet or starting new supplements.